Our Quality Assurance Gives You Peace of Mind
At Machining Quote, we understand that a rigorous quality inspection process is critical to ensure that each part meets precise engineering standards and performance requirements.

Machining Quote is Making Your Custom Parts to Your Specifications
Our Machining Quote operations boast accreditations from ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485:2016, and AS9100D, comply with ISO 2768 standards, and maintain ITAR registration. We have invested heavily in an advanced precision workshop, bolstered by our skilled in-house application engineering team and the rigorous standards upheld by the Machining Quote Quality Assurance Lab. This integration ensures unparalleled support and quality assurance for every component we dispatch. Our Quality Assurance Lab is equipped with highly trained quality engineers who consistently enhance our certification documentation and virtual inspection protocols. This meticulous approach guarantees that every order meets the highest standards of precision and reliability, affirming our commitment to excellence in metrology.
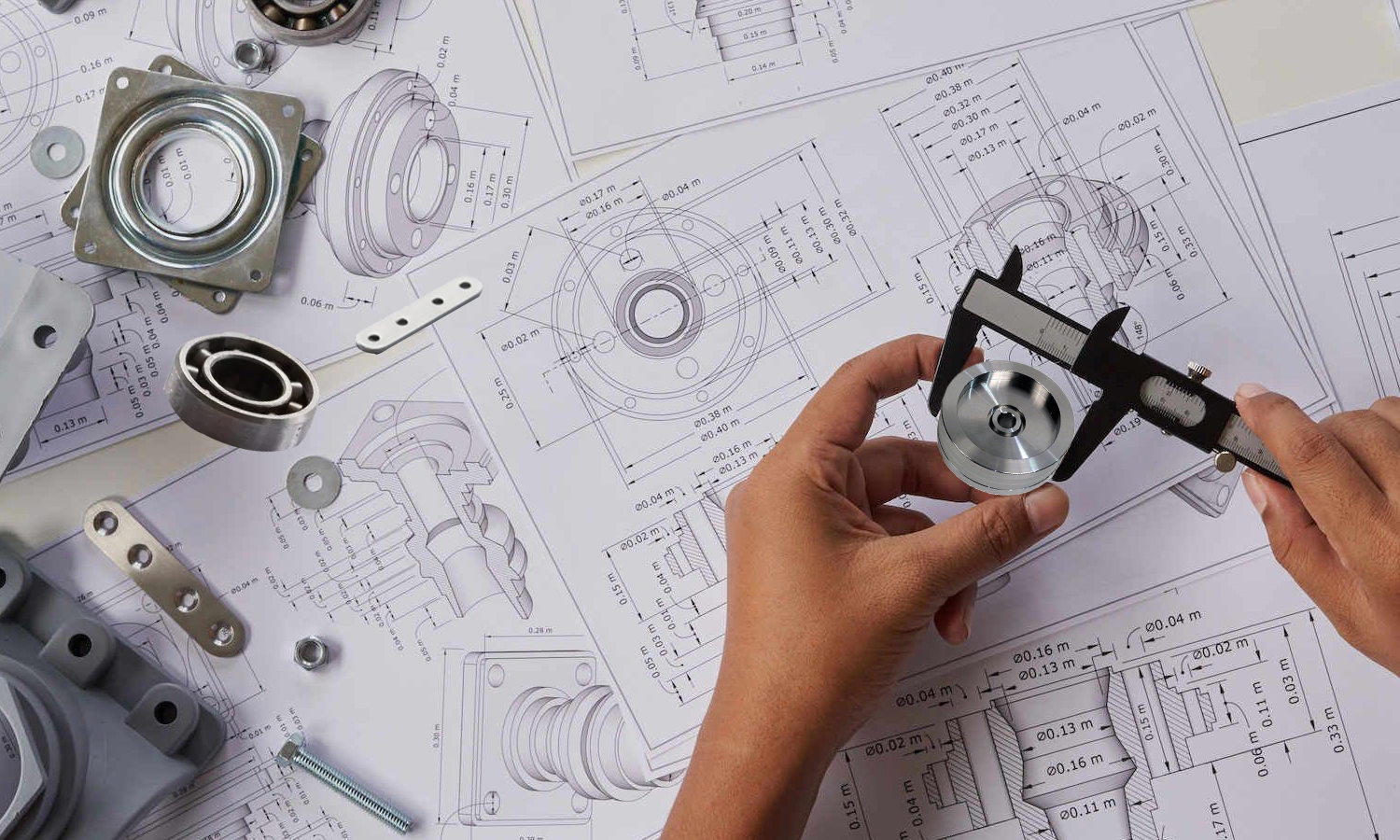
Design Validation
Pre-Production Software Checks: Utilize Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to meticulously verify the design parameters. This involves checking dimensions, tolerances, and potential stress points to ensure the part can be manufactured without errors.
Simulation: Run simulations of the machining process using the CAD/CAM data. This helps identify potential issues with tool paths or machine settings that could affect the final product’s quality.
Prototype Testing: Create prototype parts when necessary to test the design in real-world conditions. This can reveal practical challenges and performance issues that may not be apparent from digital models.
Material Inspection
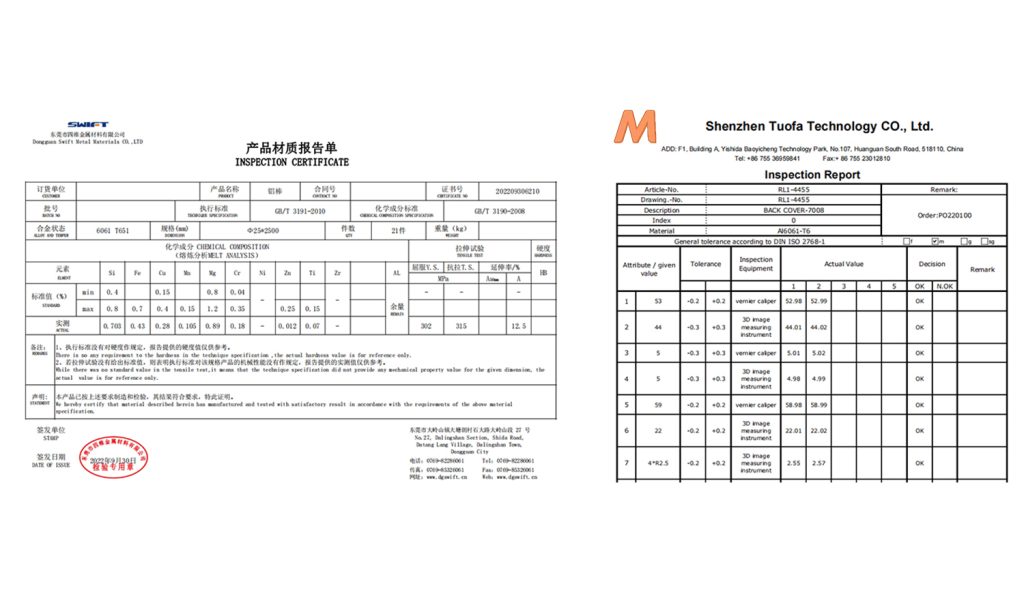
Certification and Compliance: Verify that all materials come with the proper certifications and meet industry standards such as ASTM or ISO.
Physical Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection for material defects such as cracks, impurities, or inconsistencies using visual and non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic testing.

In-Process Monitoring
Automated Monitoring Systems: Use CNC machines equipped with sensors that provide real-time feedback on cutting forces, temperature, and tool wear. This data helps adjust processing parameters dynamically to maintain optimal machining conditions.
Quality Gates: Establish checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process where parts are checked against quality standards to catch and rectify errors early in production.
Initial Inspection
Dimensional Verification: Use precision measuring tools like digital calipers, micrometers, and height gauges to ensure all dimensions meet the design specifications.
Geometrical Tolerances: Check geometric tolerances using advanced metrology equipment such as laser scanners that can quickly and accurately measure complex shapes and surfaces.
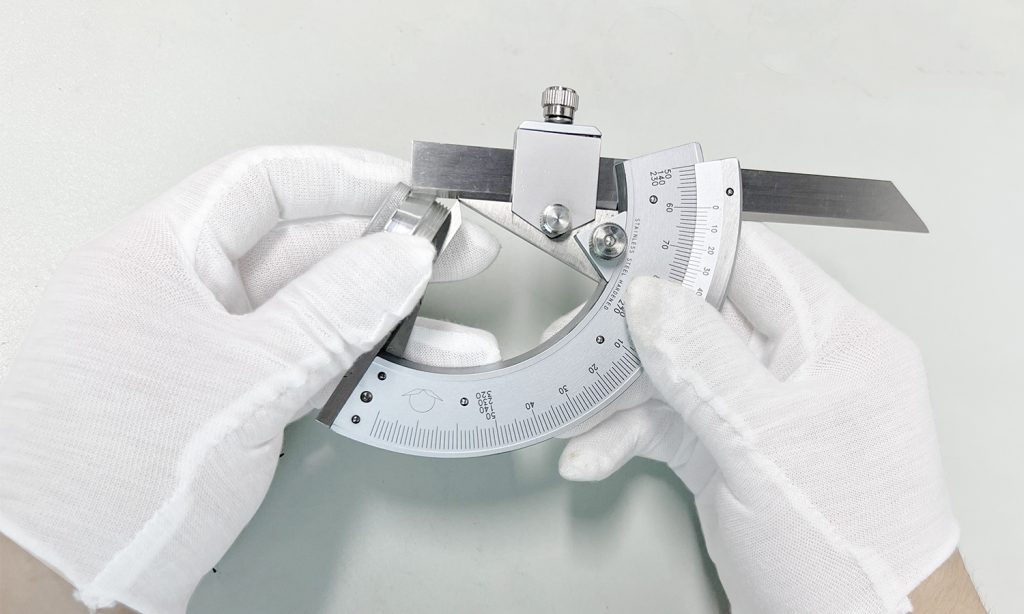
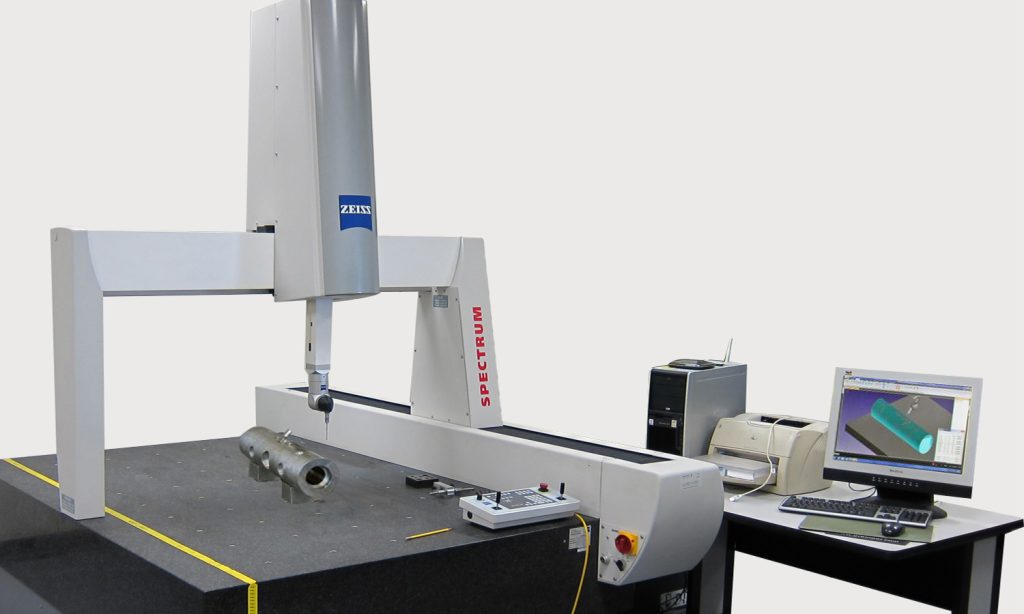


Precision Measurement
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM): Employ CMMs for high-precision inspections of critical dimensions and alignment, providing detailed reports on each part’s conformance to specifications.
Optical and Laser Systems: Use these for non-contact measurements, especially useful for parts with fine details or sensitive surfaces.
Surface and Functionality Tests
Surface Roughness: Measure surface finish using profilometers to ensure it meets required smoothness or texture specifications.
Load and Stress Tests: Simulate operational loads and stress through physical or virtual tests to ensure the part will perform as expected under real conditions.
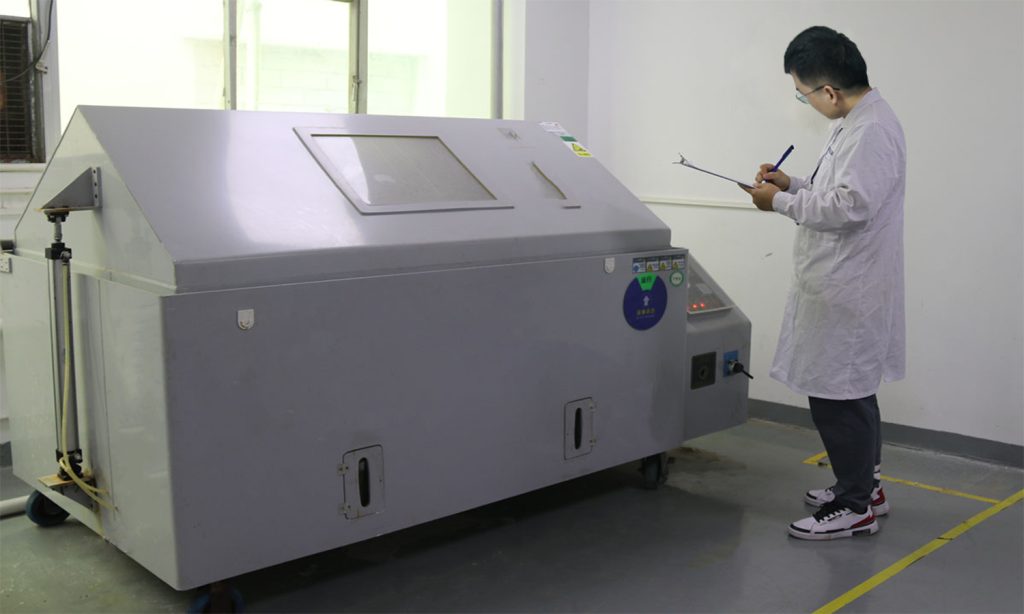
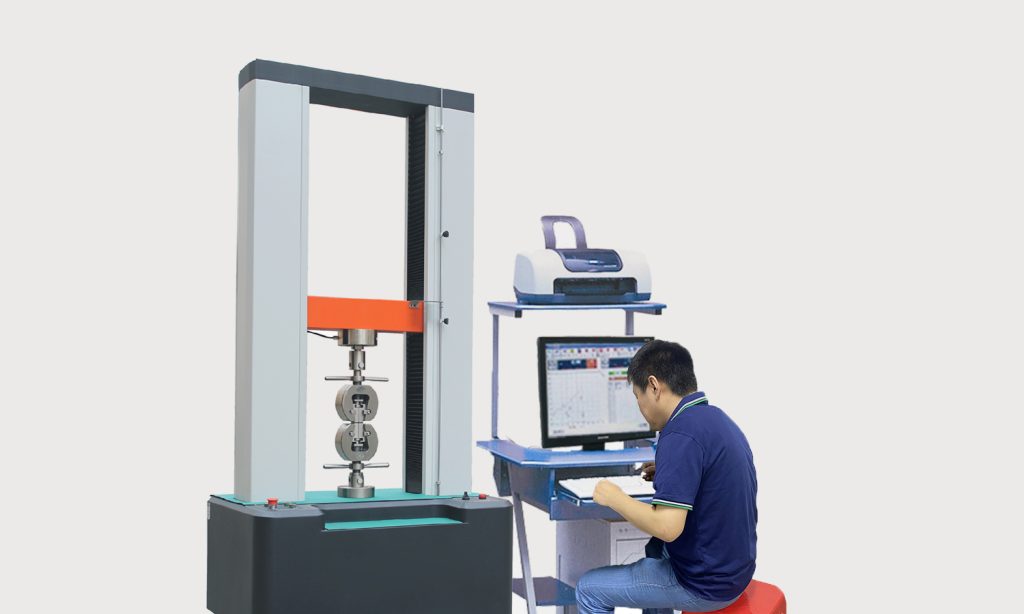


Fatigue and Stress Testing
Extended Use Simulations: Perform accelerated life testing to predict how parts will fare over time, identifying potential failure modes and life expectancy.
Advanced Analysis Software: Utilize Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tools to model and analyze stresses and strains, providing a deeper understanding of how parts will behave under different load scenarios.
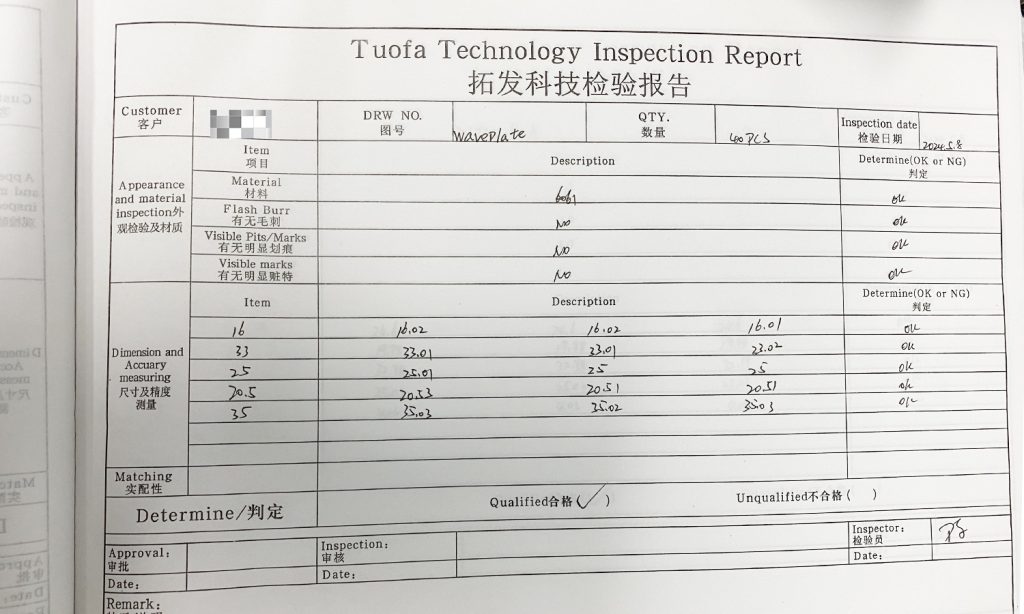
Final Inspection and Documentation
Comprehensive Review: Ensure a senior quality inspector conducts a final quality review to verify all aspects of the part’s construction and finish.
Documentation and Traceability: Keep detailed records of all tests and inspections, establishing a traceability matrix that links each part to its specific batch, material, and production details.
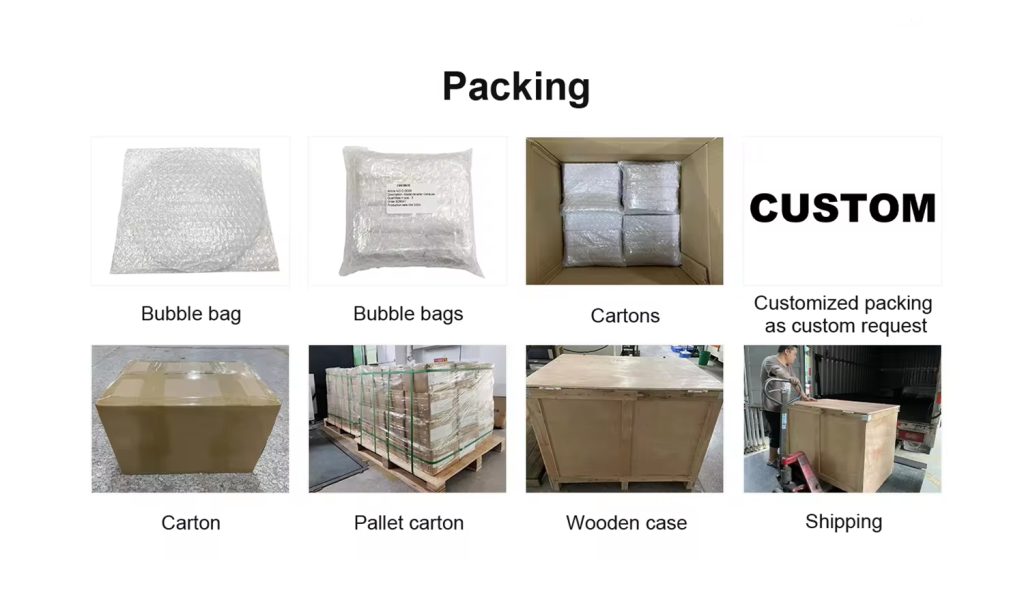
Packaging and Shipping
Custom Packaging Solutions: Design packaging that supports and protects the parts based on their size, shape, and sensitivity, ensuring they reach the customer without any damage.
Handling Instructions: Include clear handling and unpacking instructions to prevent damage during final installation or use.
